大模型实战篇:设计模式–,的并行处理器
通过构建有向无环图DAG来表示任务之间的依赖关系,LLMCompiler能够实现任务的并行执行,从而大幅降低总执行时间。本文将详细介绍LLMCompiler的原理、实现过程以及其在实际应用中的优势。
在上篇文章《AI大模型实战篇:AIAgent设计模式–Plan&Execute》中,风叔结合原理和具体源代码,详细介绍了AIAgent设计模式中的Plan-and-Execute。但是Plan-and-execute的局限性在于,每个任务是按顺序执行的,这可能会导致总执行时间的增加。
一种有效改进的办法是将每个任务表示为有向无环图DAG,这样可以让多个任务并行执行,大幅降低执行总时间。
这就是本篇文章风叔将为大家介绍的AIAgent设计模式,LLMCompiler。
01LLMCompiler的概念
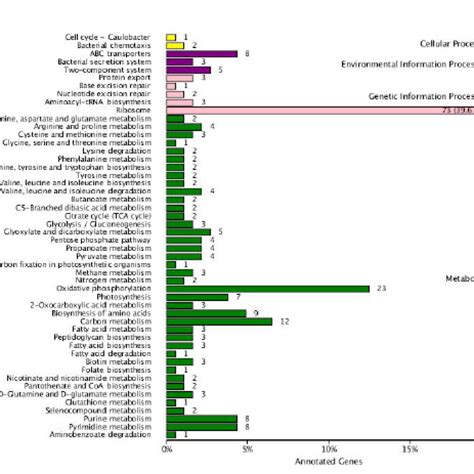
LLMCompiler是伯克利大学的SqueezeAILab于2023年12月提出的新项目。这个项目在ReWOO引入的变量分配的基础上,进一步训练大语言模型生成一个有向无环图(DirectedAcyclicGraph,DAG,如下图所示)类的规划。DAG可以明确各步骤任务之间的依赖关系,从而并行执行任务,实现类似处理器“乱序执行”的效果,可以大幅加速AIAgent完成任务的速度。
1.LLMCompiler设计模式主要有以下组件:
2.下图是LLMCompiler的原理:
02LLMCompiler的实现过程
下面,风叔通过实际的源码,详细介绍LLMCompiler模式的实现方法。
第一步构建工具Tools
首先,我们要定义Agent需要使用的工具。在这个例子中,我们将使用搜索引擎 计算器这两个工具。
_get_pass(“TAVILY_API_KEY”)
第二步构建Planner
Planner接收用户输入,并生成一个待执行的任务清单的DAG。
以下代码构建了Planner的提示模板,并将其与LLM和输出解析器组合在一起,输出解析器处理以下形式的任务列表。在Planner中,我们同时定义了replanner的Prompt,这个prompt提出了三项核心的约束
defcreate_planner(
llm:BaseChatModel,tools:Sequence[BaseTool],base_prompt:ChatPromptTemplate
):
tool_descriptions=“n”.join(
f”{i 1}.{tool.description}n”
fori,toolinenumerate(
tools
)# 1tooffsetthe0startingindex,wewantitcountnormallyfrom1.
)
planner_prompt=base_prompt.partial(
replan=””,
num_tools=len(tools)
1,#Addonebecausewe’readdingthejoin()toolattheend.
tool_descriptions=tool_descriptions,
replanner_prompt=base_prompt.partial(
replan=’–Youaregiven“PreviousPlan”whichistheplanthatthepreviousagentcreatedalongwiththeexecutionresults‘
“(givenasObservation)ofeachplanandageneralthought(givenasThought)abouttheexecutedresults.”
‘YouMUSTusetheseinformationtocreatethenextplanunder“CurrentPlan”.n’
‘–WhenstartingtheCurrentPlan,youshouldstartwith“Thought”thatoutlinesthestrategyforthenextplan.n’
”–IntheCurrentPlan,youshouldNEVERrepeattheactionsthatarealreadyexecutedinthePreviousPlan.n”
”–Youmustcontinuethetaskindexfromtheendofthepreviousone.Donotrepeattaskindices.”,
num_tools=len(tools) 1,
defshould_replan(state:list):
#Contextispassedasasystemmessage
returnisinstance(state[-1],SystemMessage)
defwrap_messages(state:list):
return{“messages”:state}
defwrap_and_get_last_index(state:list):
next_task=0
formessageinstate[::-1]:
ifisinstance(message,FunctionMessage):
next_task=message.additional_kwargs[“idx”] 1
break
state[-1].content=state[-1].content f”–Begincountingat:{next_task}”
这个部分负责安排任务,它接收以下格式的数据流。
tool:BaseTool,
dependencies:number[]
其核心思想是,一旦满足依赖关系,就开始执行工具,可以通过多线程实现。下面这段代码的关键就在于schedule_tasks,会将所有任务处理成有向无环图。在当前任务存在尚未完成的依赖关系时,放入pendingtask;在当前任务所有依赖关系都已完成时,执行任务。
@as_runnable
defschedule_task(task_inputs,config):
task:Task=task_inputs[“task”]
observations:Dict[int,Any]=task_inputs[“observations”]
try:
observation=_execute_task(task,observations,config)
exceptException:
importtraceback
observations[task[“idx”]]=observation
defschedule_pending_task(task:Task,observations:Dict[int,Any],retry_after:float=0.2):
whileTrue:
deps=task[“dependencies”]
ifdepsand(any([depnotinobservationsfordepindeps])):
#Dependenciesnotyetsatisfied
time.sleep(retry_after)
continue
schedule_task.invoke({“task”:task,“observations”:observations})
defschedule_tasks(scheduler_input:SchedulerInput)->List[FunctionMessage]:
“””GroupthetasksintoaDAGschedule.”””
tasks=scheduler_input[“tasks”]
args_for_tasks={}
messages=scheduler_input[“messages”]
observations=_get_observations(messages)
task_names={}
originals=set(observations)
futures=[]
retry_after=0.25#Retryeveryquartersecond
withThreadPoolExecutor()asexecutor:
fortaskintasks:
task_names[task[“idx”]]=(
task[“tool”]ifisinstance(task[“tool”],str)elsetask[“tool”].name
args_for_tasks[task[“idx”]]=task[“args”]
if(
#Dependsonothertasks
deps
and(any([depnotinobservationsfordepindeps]))
futures.append(
executor.submit(
schedule_pending_task,task,observations,retry_after
else:
#Nodepsoralldepssatisfied,canschedulenow
schedule_task.invoke(dict(task=task,observations=observations))
#futures.append(executor.submit(schedule_task.invokedict(task=task,observations=observations)))
#Alltaskshavebeensubmittedorenqueued
#Waitforthemtocomplete
wait(futures)
#Convertobservationstonewtoolmessagestoaddtothestate
new_observations={
k:(task_names[k],args_for_tasks[k],observations[k])
forkinsorted(observations.keys()–originals)
}
tool_messages=[
FunctionMessage(
name=name,content=str(obs),additional_kwargs={“idx”:k,“args”:task_args}
fork,(name,task_args,obs)innew_observations.items()
]
importitertools
defplan_and_schedule(state):
messages=state[“messages”]
tasks=planner.stream(messages)
#Beginexecutingtheplannerimmediately
tasks=itertools.chain([next(tasks)],tasks)
exceptStopIteration:
#Handlethecasewheretasksisempty.
tasks=iter([])
scheduled_tasks=schedule_tasks.invoke(
{
“messages”:messages,
“tasks”:tasks,
return{“messages”:[scheduled_tasks]}
第四步构建Joiner
前面我们构建了Planner和TaskFetchingUnit,下一步我们需要构建Joiner来处理工具的输出,以及决定是否需要使用新的计划并开启新的循环。
classFinalResponse(BaseModel):
“””Thefinalresponse/answer.”””
response:str
classReplan(BaseModel):
feedback:str=Field(
description=”Analysisofthepreviousattemptsandrecommendationsonwhatneedstobefixed.”
classJoinOutputs(BaseModel):
“””Decidewhethertoreplanorwhetheryoucanreturnthefinalresponse.”””
thought:str=Field(
description=”Thechainofthoughtreasoningfortheselectedaction”
action:Union[FinalResponse,Replan]
joiner_prompt=hub.pull(“wfh/llm-compiler-joiner”).partial(
examples=””
)#Youcanoptionallyaddexamples
llm=ChatOpenAI(model=”gpt-4-turbo-preview”)
runnable=create_structured_output_runnable(JoinOutputs,llm,joiner_prompt)
如果Agent需要继续循环,我们需要选择状态机内的最新消息,并按照Planner的要求输出相应的格式。
return{“messages”:selected[::-1]}
joiner=select_recent_messages|runnable|_parse_joiner_output
input_messages=[HumanMessage(content=example_question)] tool_messages
joiner.invoke(input_messages)
下面,我们构建流程图,将Planner、TaskFetchingUnit、Joiner等节点添加进来,循环执行并输出结果。
classState(TypedDict):
messages:Annotated[list,add_messages]
graph_builder=StateGraph(State)
graph_builder.add_node(“plan_and_schedule”,plan_and_schedule)
graph_builder.add_node(“join”,joiner)
graph_builder.add_edge(“plan_and_schedule”,“join”)
defshould_continue(state):
ifisinstance(messages[-1],AIMessage):
returnEND
return“plan_and_schedule”
graph_builder.add_conditional_edges(
start_key=”join”,
#Next,wepassinthefunctionthatwilldeterminewhichnodeiscallednext.
condition=should_continue,
graph_builder.add_edge(START,“plan_and_schedule”)
chain=graph_builder.compile()
总结
通过前面三篇文章,大模型实战篇:设计模式–,的并行处理器按照递进关系,风叔依次介绍了REWOO、Plan-and-Execute和LLMCompiler三种更侧重规划能力的AIAgent设计模式。从最初的ReAct模式出发,加入规划能力即演变成REWOO;再加上Replan能力即演变成Plan-and-Execute;最后再加上DAG和并行处理能力,即演变成LLMCompiler。
题图来自Unsplash,基于CC0协议。